Gynecomastia vs. Fat: Which One Do You Have?
When you notice your chest looks enlarged, it’s natural to wonder: Is it gynecomastia or just excess fat? Gynecomastia vs. fat is an important distinction to make, as gynecomastia is marked by firm glandular tissue, whereas ordinary chest fat is softer. This article strips away the confusion, pinpointing how to tell gynecomastia apart from fat, what causes each condition, and what you can do about it.
Key Takeaways
- Gynecomastia is characterized by the enlargement of breast glands in men and presents with symptoms such as pain, sensitivity, and firm tissue, distinguishing it from regular chest fat that accumulates due to weight gain and lifestyle factors.
- Treatment options for gynecomastia include male breast reduction surgery, which involves removal of excess fat, breast tissue, and skin, whereas lifestyle changes and exercises are recommended for dealing with regular chest fat.
- Hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated estrogen levels or disproportionate ratios with testosterone, are primary contributors to gynecomastia, while diet and exercise are key factors influencing the amount of chest fat.
Deciphering Gynecomastia and Regular Chest Fat
Gynecomastia is a term that refers to the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in men. This condition is attributed to the growth of glandular breast tissue, which presents a rubbery or firm texture. On the other hand, regular chest fat refers to the adipose tissue that gathers in the chest region, exhibiting similar characteristics to fat found in other parts of the body. Unlike gynecomastia, it is softer, more evenly distributed, and is impacted by factors such as weight and lifestyle.
While they may appear similar, gynecomastia and regular chest fat have distinct characteristics. Gynecomastia is typically characterized by a rubbery or firm lump in the chest, which can be mistaken for regular chest fat that is softer and more evenly distributed. In some cases, surgical treatment may be necessary to address gynecomastia.
Recognizing the Signs: Gynecomastia or Chest Fat?
Recognizing the signs of gynecomastia can help differentiate it from regular chest fat. Symptoms of gynecomastia include:
- Pain
- Swollen breast tissue
- Tender or sensitive breasts
- Sensitive nipples that may become sore when they rub against clothes
- A lump or fatty tissue beneath the nipple that may be tender to touch
- Uneven growth of breasts
Gynecomastia is caused by the growth of breast glands, unlike regular chest fat.
In contrast, chest fat does not typically present with these symptoms. Instead, it is softer and spreads more evenly across the chest. Understanding these distinctions can help you better identify whether you are dealing with gynecomastia or chest fat, and subsequently decide on the most appropriate course of treatment.
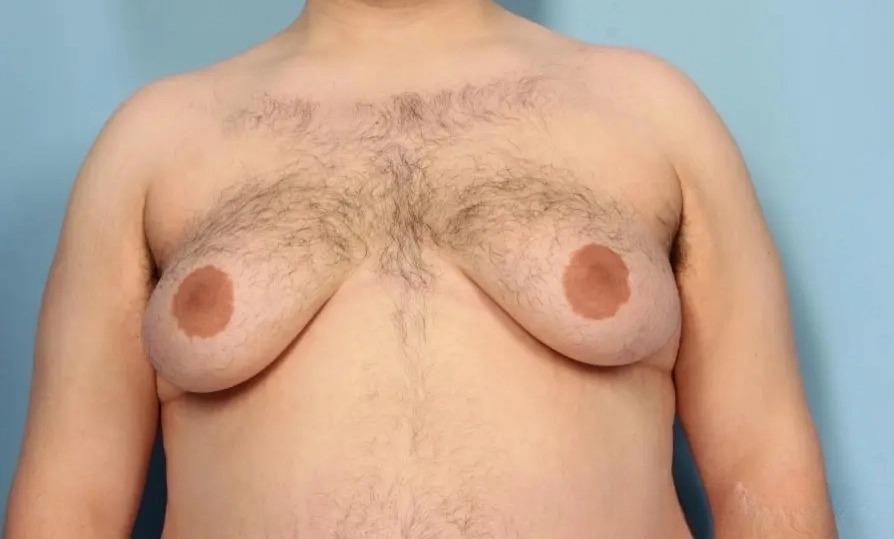
The Root Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is primarily attributed to imbalances in the hormones estrogen and testosterone, especially when estrogen levels are elevated or not properly balanced with testosterone levels. This hormonal imbalance can lead to an increase in breast tissue, resulting in gynecomastia.
Several medical conditions can also lead to the development of gynecomastia. These include:
- Hypogonadism
- Aging
- Liver or lung cancer
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Overactive thyroid
- Chronic conditions like cirrhosis and renal insufficiency
Furthermore, the use of specific medications or illicit drugs has been linked to the development of gynecomastia.
Why Excess Body Fat Does Not Equal Gynecomastia
It’s worth noting that excess body fat doesn’t necessarily imply gynecomastia. Gynecomastia is identified by the presence of excessive glandular tissue resulting in chest swelling and hard lumps, whereas excess body fat in the chest does not entail glandular tissue growth.
The criteria used to distinguish gynecomastia from regular chest fat include:
- The presence of glandular breast tissue in gynecomastia
- The shape of the chest (round and proportioned in gynecomastia, saggy or droopy in chest fat)
- The responsiveness to lifestyle modifications (gynecomastia is predominantly unresponsive to lifestyle changes)
Gynecomastia and excess body fat differ fundamentally; the former involves excess glandular breast tissue in the pectoral area, while the latter constitutes adipose tissue or fat in the chest area, usually tied to overall weight gain. In some cases, individuals may experience a combination of both excess breast tissue and excess chest fat, leading to a more complex presentation of the issue.
Navigating Treatment Options for Gynecomastia vs. Fat
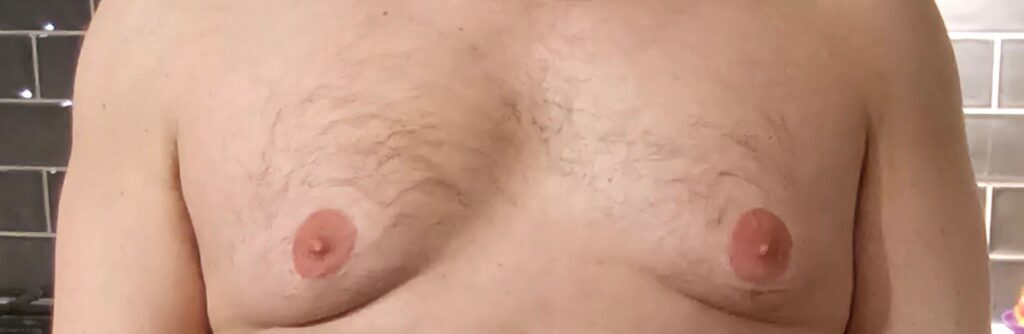
There are several treatment options available for those dealing with gynecomastia and chest fat, ranging from surgical interventions to lifestyle changes. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity of the condition, individual health status, and personal preferences.
Male Breast Reduction Surgery
Male breast reduction surgery is a common treatment option for gynecomastia. The surgery involves the extraction of surplus fat, breast tissue, and skin from the breasts to diminish breast size and enhance chest contours. The approach for this surgery is customized to the specific needs of the individual, considering the severity of their gynecomastia.
The procedure entails:
- Creating small incisions on each side of the chest, typically around the pigmented edge of the areola or under the armpit
- Eliminating excess tissue using liposuction
- Reshaping the chest to achieve the desired form
It has been shown to be an efficacious treatment for gynecomastia, aiding in the reduction of enlarged male breast tissue and the elimination of excess fat on the chest.
Lifestyle Changes for Chest Fat Reduction
Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and physical activity, can also influence the appearance of chest fat. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet can aid in reducing chest fat and potentially prevent the onset of gynecomastia.
Exercises recommended for reducing chest fat include:
- Pushups
- Bench press
- Cable-cross
- Dumbbell pull over
- Parallel-bar dips
Incorporating these exercises into your routine can aid in reducing chest fat and enhancing the appearance of the chest. Additionally, reducing alcohol consumption and refraining from smoking can also contribute to chest fat reduction and overall health improvement.
The Role of Hormones in Gynecomastia and Weight Gain
Hormones significantly influence the development of gynecomastia and weight gain. The onset of gynecomastia is primarily due to hormonal imbalances, particularly when estrogen levels surpass or are not in equilibrium with testosterone levels.
Additionally, testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining a balance with estrogen. Low levels of testosterone not only contribute to the development of gynecomastia but also have the potential to influence body weight. This demonstrates how hormonal imbalances can have broad impacts on the body, including the development of gynecomastia and changes in body weight.
Surgical Solutions: Understanding Male Breast Reduction
Surgical solutions for treating gynecomastia include liposuction and surgical excision. Liposuction involves the removal of surplus fat and glandular tissue, often in combination with skin tightening methods to enhance aesthetic results.
On the other hand, the excision technique entails the surgical extraction of glandular breast tissue or surplus skin to address gynecomastia. This is typically carried out through an infra-areolar incision around the nipple area or a single transverse incision made through the nipple.
Achieving a Toned Chest: Exercise Regimen for Reducing Chest Fat
An exercise regimen specifically aimed at the chest can significantly reduce chest fat and help attain a toned physique. The recommended exercises for reducing chest fat include:
- Pushups
- Bench press
- Cable-cross
- Dumbbell pull over
- Dumbbell incline bench press
Incorporating these exercises into your routine can aid in reducing chest fat and enhancing the appearance of the chest.
In addition to specific exercises, regular cardio activities like running, swimming, or cycling also contribute to decreasing overall body fat, subsequently leading to a reduction in chest fat. Exercise should be consistent, with a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio activity per week to observe noticeable changes.
When Diet and Exercise Aren’t Enough: Considering Liposuction
For some individuals, diet and exercise may not be sufficient to reduce chest fat. Liposuction can be considered a viable option in these cases. It may help to achieve the desired results. The liposuction procedure for chest fat reduction is a surgical process that involves the extraction of surplus fat from the breast area. This procedure is often carried out as a component of gynecomastia surgery.
Liposuction carries potential risks, including bleeding and possible alterations in fat distribution if weight is gained after the procedure. However, it can be advantageous in diminishing the visibility of surplus fat in the chest area, even for individuals who sustain a healthy weight.
After liposuction, the recovery time may vary but is generally considered to be a part of the overall recovery period following gynecomastia surgery.
Addressing Misconceptions: Pseudo Gynecomastia and ‘Man Boobs’
There are several misconceptions surrounding the terms ‘pseudo gynecomastia’ and ‘man boobs.’ The term ‘man boobs’ refers to the medical condition called gynecomastia, characterized by an increase in the amount of breast gland tissue in boys or men, often caused by hormonal imbalance.
Pseudo gynecomastia, also referred to as false gynecomastia, is distinguished by the enlargement of male breasts primarily caused by an accumulation of fat, as opposed to the augmented breast gland tissue observed in true gynecomastia, resulting in a soft, breast-like appearance. Clearing these misconceptions is crucial in understanding the true nature of these conditions and seeking appropriate treatment.
The Psychological Impact of Gynecomastia and Chest Fat

Beyond the physical manifestations, gynecomastia and chest fat can have significant psychological implications. Research has indicated that gynecomastia can have a substantial adverse effect on psychosocial factors, including:
- well-being
- social interactions
- body image
- self-esteem
- overall quality of life
These psychological impacts underscore the importance of addressing gynecomastia and chest fat from a holistic perspective. Treatment should aim not only to alleviate physical symptoms but also to bolster psychological well-being, underscoring the importance of empathy and understanding in the treatment process.
Choosing a Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon for Gynecomastia Treatment
When contemplating surgery for gynecomastia, choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon is of utmost importance. This guarantees the involvement of a reputable professional equipped with the essential skills and qualifications. These surgeons are affiliated with esteemed organizations such as the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) and are capable of delivering safe and controlled surgical procedures.
The success rates for gynecomastia treatment by both board-certified plastic surgeons and non-board-certified surgeons are notably high, with satisfaction rates falling within the range of 92.6% to 92.9%. However, opting for a board-certified surgeon ensures adherence to stringent safety and ethical standards, providing patients with added assurance.
“Gynecomastia vs. Fat” Summary
In conclusion, understanding the difference between gynecomastia and chest fat is crucial in identifying the appropriate treatment options and managing expectations. From hormonal imbalances and the impact of lifestyle changes to surgical interventions and the importance of choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon, every aspect plays a significant role in the journey towards recovery and improved quality of life.
FAQS
References
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gynecomastia
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gynecomastia/symptoms-causes/syc-20351793
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/16227-enlarged-male-breast-tissue-gynecomastia

